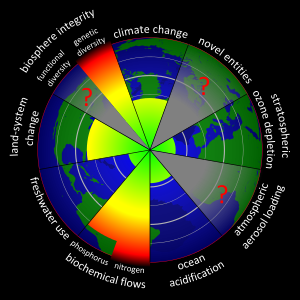
Planetary Boundaries 2015
Planetary boundaries is the central concept in an Earth system framework proposed by a group of Earth system and environmental scientists led by Johan Rockström from the Stockholm Resilience Centre and Will Steffen from the Australian National University.
In 2009, the group proposed a framework of “planetary boundaries” designed to define a “safe operating space for humanity” for the international community, including governments at all levels, international organizations, civil society, the scientific community and the private sector, as a precondition for sustainable development.
This framework is based on scientific research that indicates that since the Industrial Revolution, human actions have gradually become the main driver of global environmental change. The scientists assert that once human activity has passed certain thresholds or tipping points, defined as “9 planetary boundaries”, there is a risk of “irreversible and abrupt environmental change”.
Red: Beyond zone of uncertainty (high risk)
Yellow: In zone of uncertainty (increasing risk)
Green: Below boundary (safe)
Grey: Boundary not yet quantified
- Read this 2013 journal article that analysis the Planetary Boundaries framework against the Natural Step approach.
- Do you agree with the authors’ conclusions?
- Make a comment about your reasons in WEnotes
- Planetary boundaries: I agree with the author’s conclusions because…
- Planetary boundaries: I disagree with the author’s conclusions because…
You must be logged in to post to WEnotes.
Planetary boundaries is the central concept in an Earth system framework proposed by a group of Earth system and environmental scientists led by Johan Rockström from the Stockholm Resilience Centre and Will Steffen from the Australian National University.
In 2009, the group proposed a framework of “planetary boundaries” designed to define a “safe operating space for humanity” for the international community, including governments at all levels, international organizations, civil society, the scientific community and the private sector, as a precondition for sustainable development.
This framework is based on scientific research that indicates that since the Industrial Revolution, human actions have gradually become the main driver of global environmental change. The scientists assert that once human activity has passed certain thresholds or tipping points, defined as “9 planetary boundaries”, there is a risk of “irreversible and abrupt environmental change”.
Red: Beyond zone of uncertainty (high risk)
Yellow: In zone of uncertainty (increasing risk)
Green: Below boundary (safe)
Grey: Boundary not yet quantified
WEnote activity
You must be logged in to post to WEnotes.
Content is available under the
Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike License.
Privacy Policy | Authors